
SQL Where Clause
SQL Where Clause
In this Blog you will learn how to Fetch Filter Data from Database Tables using SQL Where Clause and also learn to specify a condition while fetching the data from a single table or by joining with multiple tables.
WHERE clause
A where condition is optional part in SELECT and UPDATE & DELETE statements.
In the Where clause let you selected the rows based on the Boolean expression. If the expression is “TRUE” then results will be returned.
Note: WHERE clause return after the Oracle FROM clause.
Here we can use the operators in where the condition
Basic operators :
- =( EQUAL), <(LESS THEN)
- => (GREATER THEN EQUAL)
- =< (LESS THEN EQUAL)
- <> (NOT EQUAL)
Advanced operators:
- IN
- ALL
- BETWEEN
- LIKE
- AND
- OR
WHERE clause can be used in JOINS also Like
- INNER JOIN
- OUTER JOIN
- LEFT JOIN
- RIGHT JOIN
It can be used in DATE Range
Syntax:
Select * from table name WHERE column_name operational value.
Example:
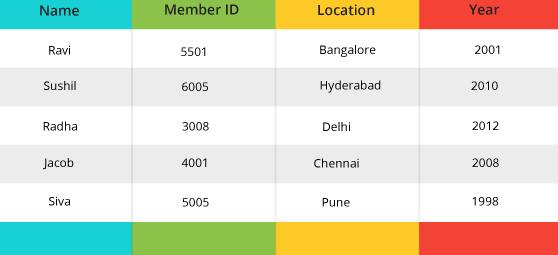
Postal table with the data.
Select * from postal;
SELECT Statement
Select * from postal where MemberID=5005;
Output:

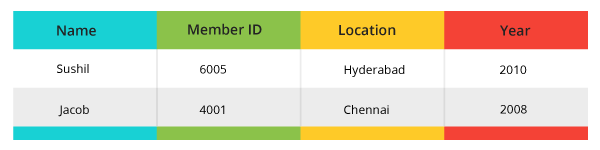
Select * from postal where MemberID IN (6005, 4001);
Output:
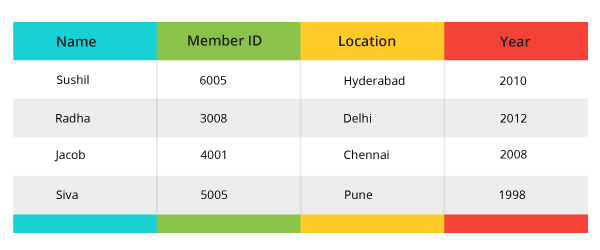
Select * from postal where Location LIKE ’%Del%’;
Output:
UPDATE Statement
- Update postal
Set location=’Mumbai’
Where Member ID=’5005’;
Commit;
- Select * from postal where MemberID=5005;
Output:
Delete from postal
Where Name= ‘Ravi’;
Commit;




 +1 201-949-7520
+1 201-949-7520 +91-9707 240 250
+91-9707 240 250