
Types of Errors in Java
Types of Errors in Java
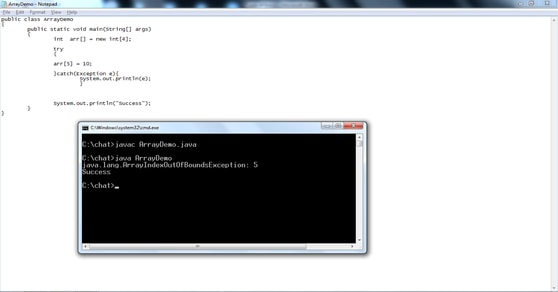
Run Time errors are occurs during execution of program. Java compiler will not detect Run Time errors. Only Java Virtual Machine (JVM) will detect it while executing the program.
Example:
The below program will produce the run time error.
class RunTimeErrorDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = new int[4];
arr[5] = 100;
System.out.println("Success");
}
}
|
Example:
class RunTimeErrorDemo{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
int arr[] = new int[4];
arr[5] = 100;
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Success");
}
}
|
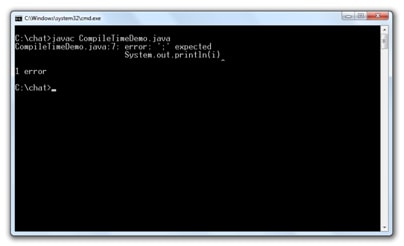
Compile Time Error:
Errors that occur during compiling the program and if there any syntax error in the program like missing semicolon at the end of a statement or curly braces etc., then the Java compiler displays the error on to the screen.
Example:
class CompileTimeDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i=10;
//Missing semicolon at the end of statement
System.out.println(i)
}
}
|
Logical Error:
In Java logical error is nothing but when a program is compiled and executed without any error but not producing any result is called as logical error. These errors can’t be detected by neither compiler nor JVM.
Exception:
An exception is nothing but during execution of a program any errors occur due to some reasons and that causes an abnormal termination of the program.
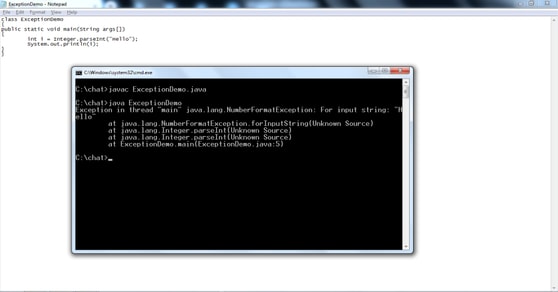
In Java there are two types of exceptions.
- CompileTime Exception
- RunTime Exception
CompileTime Exception (Checked Exception):
These exceptions will occur during compile time itself
RunTime Exception (Unchecked Exception):
These exceptions will not be detected during compilation and will be detected by JVM during execution of the program.
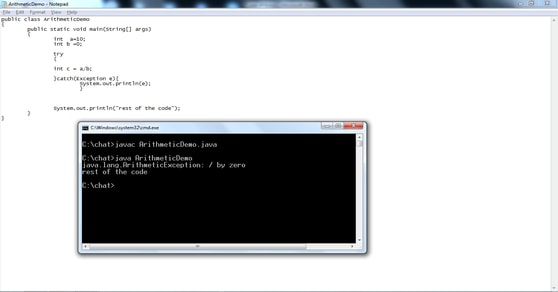
Example:
Arithmetic Exception:


 +1 201-949-7520
+1 201-949-7520 +91-9707 240 250
+91-9707 240 250