
Indexes in SQL
Indexes are used in fetching records from the database more quickly. It improves query performance by applying indexes on fields. Hence the retrieval of values on fields becomes very fast. Index generally boost your query performance with SELECT queries and WHERE clauses but it give an impact on INSERT and UPDATE statements as it slows down the data manipulation operations
Limitation of applying index on a table :
Index applied tables take more time to compare to the table with without index
Single Column Indexes
Create Index: It applies an index on a table with duplicate values in the field
Syntax :
CREATE INDEX <index name>
ON <table name> (<column1>);
Let’s understand how to apply single-column index in SQL with an example,
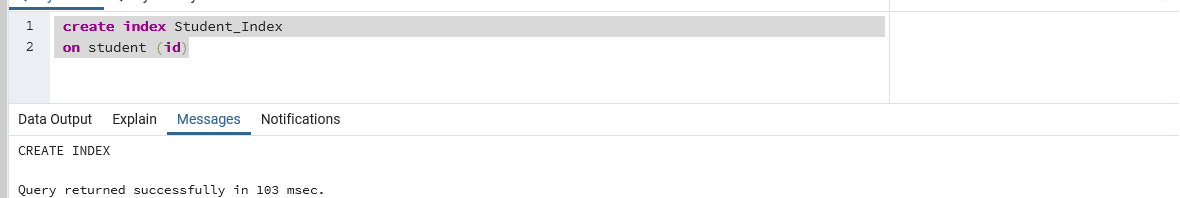
In the above example, we have created an index named “Student_Index” on the “id” field of the “student” table. As we have passed only a single field “id”, it will create an index on single column of the “student” table. This index can be used & fetch all the duplicate entries of “id” column in “student” table
Unique Indexes
Create Unique Index: It applies the index on a table without duplicate values in the field
Syntax :
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX <index name>
ON <table name> (<column1>);
Let’s understand how to apply unique index in SQL with an example,
In the above example, we have created an index named “Student_Index” on the “id” field of the “student” table. As we have passed only a single field “id”, it will create an index on a single column of the “student” table. This index can be used & fetch only unique entries of “id” column in “student” table
Composite Indexes
Create a Composite Index: It applies indexes on two or multiple columns of the table.
Syntax :
CREATE INDEX <index name>
ON <table name> (<column1>, <column2>, …);
Let’s understand how to apply the composite index in SQL with an example,
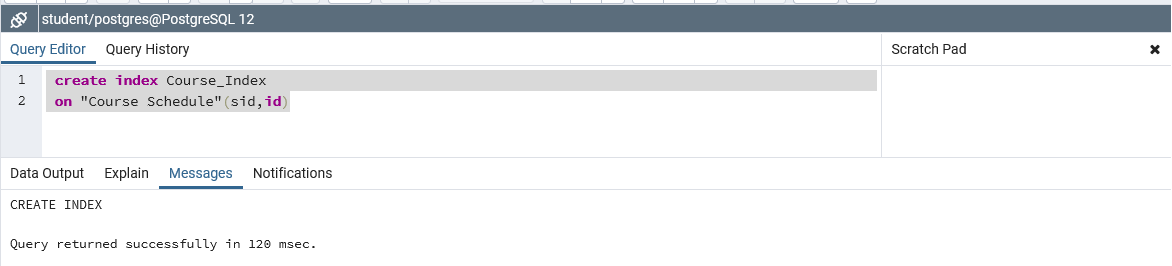
In the above example, we have created an index named “Course_Index” on the “id” field of the “Course Schedule” table. As we have passed two fields “sid” & “id” , it will create an index on two columns of the “student” table. This index can be used & fetch all entries of “id” & “sid” columns in “Course_Index” table
Implicit Indexes
These indexes are automatically created by DBMS system whenever an object is created with primary & unique constraints Indexes can be removed from tables, Once we remove the index from tables there will not be any impact on records of the table
Drop Index: It removes index from the table
Syntax :
DROP INDEX table_name.index_name;
Let’s understand how to apply unique index in SQL with an example,
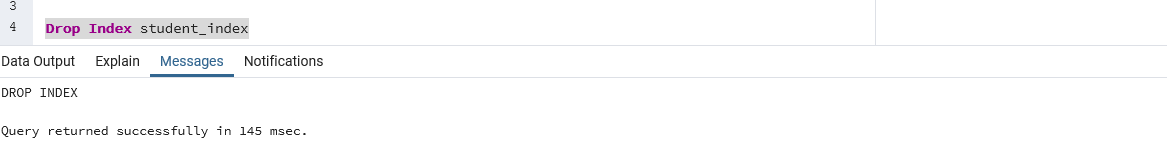
In the above example, we are dropping an index named “student_index”. Once we drop the index from the table, there will not be any impact on the data values of fields in the table.
Where not to use index :
- Avoid applying indexes on small tables
- Avoid using indexes on transactional tables where bulk insert & update operations are scheduled
- Indexes should not be applied on a column containing higher % of null values
- Fields which are frequently changed should not be indexed


 +1 201-949-7520
+1 201-949-7520 +91-9707 240 250
+91-9707 240 250